
If you’re getting ready to apply to business school, you’re probably asking yourself: “How long should I study for the GMAT?” Can I prepare in a month? What about two? Should I just go ahead and block off six months for intense studying?
The answer to this question depends a lot on the student. Some people take the GMAT with little-to-no preparation, while others spend months preparing. It’s important to make a plan that works best for you and your goals. That way, you can maximize your score, while making sure that your study plan fits your schedule and needs, so you don’t waste time over-studying.
This guide will help you figure out how long to study for the GMAT based on what kind of score increase you’re hoping to make. From there, I’ll explain how many hours you need to study, when you should start to study, and how to create a study plan.
How Long Does It Take to Prepare for the GMAT?
Achieving a strong score on the GMAT can be a labor intensive process. According to MBA.com, most test takers spend at least 50 hours studying for the exam. That number is even higher among those aiming to score 700+.
That being said, there’s a wide variety in the amount of time people spend studying for the GMAT. Take a look at these breakdowns of time spent preparing for the test, according to the Prospective Students Survey (2014) from GMAC at mba.com.
Not sure how or what to study? Confused by how to improve your score in the shortest time possible? We've created the only Online GMAT Prep Program that identifies your strengths and weaknesses, customizes a study plan, coaches you through lessons and quizzes, and adapts your study plan as you improve.
We believe PrepScholar GMAT is the best GMAT prep program available, especially if you find it hard to organize your study schedule and don't want to spend a ton of money on the other companies' one-size-fits-all study plans.

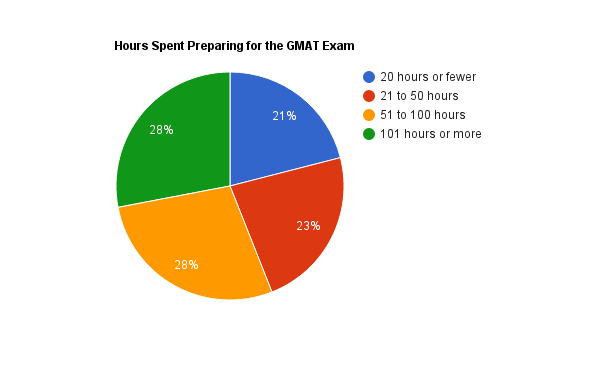
As you can see, while there’s a pretty even split between each of the pieces of that pie, most people spend over 51 hours studying for the GMAT. Let’s take a deeper look into the data from the same MBA.com survey to learn how hours spent preparing for the GMAT correspond to test scores.
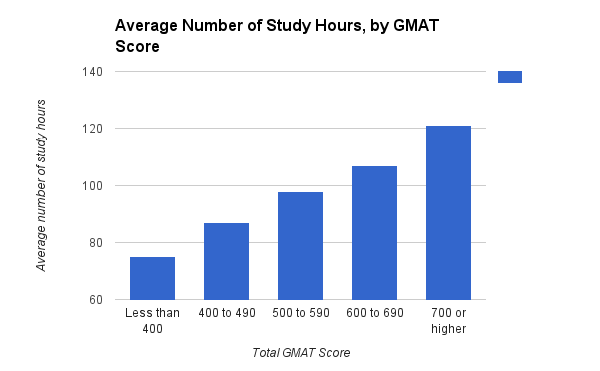
Taken together, these two charts give us a lot of information. First of all, we can see that test-takers generally prepare for at least 51 hours. We can also see that people who scored higher on the GMAT generally put in more hours preparing.
“But why are the numbers in each chart so different?” you might be asking. Well, some people might put in an insane amount of preparation hours, thus skewing the average for each score. Generally, though, the conclusion that most people study for over 50 hours holds up with each dataset.
While we can see that people scoring 700+ average the most study hours, don’t assume that studying for a certain amount of time means you’re guaranteed to get a better score. It’s important to craft a quality study plan that maximizes benefits for your time and effort. We’ll talk about that a little later in this guide.
You can see that there’s a wide range in how many hours people spend studying for the GMAT. How can you determine what’s right for you? In order to figure out how long to study for the GMAT, you need to first figure out how much you need to improve your score.
How Much Do I Need to Improve My GMAT Score?
Before you decide how long to study for the GMAT, you need to first figure out your goal score.
Step 1: Set Your Goal GMAT Score
Setting a goal GMAT score requires a bit of work. First, you need to put together a list of all the business school programs that you’d like to attend. When you’re putting together your list, think about why you would like to attend each of these programs.
Next, research the average GMAT scores of the business schools that you want to apply to. You can find this information in a number of places. Most schools share this information on the program’s admissions page. You can also try calling the admissions department if you can’t find the info there. Other third party sources, like US News, also list the average GMAT scores of many schools.
Once you’ve found the average GMAT scores for each school, add that information to your list of business programs you’re interested in. Then, find the highest average GMAT score of all the programs.
You’re going to want to set a goal score that’s about twenty points higher than the highest average GMAT score of your target programs. That means you’ll be above the average score range for all of your programs. To learn more about what makes up a good GMAT score, check out our guide “What Is a Good GMAT Score?”
Step 2: Take a GMAT Practice Test
After you’ve figured out your goal score, you need to take a practice test (if you’ve haven’t already done so) to get an idea of where you’re currently scoring.
The best way to take a GMAT practice test is to download the free GMATPrep software so you can take an official practice test. Taking an official practice test is important because it gives you the most realistic practice questions that you can see.
When you’re taking your practice test, try to replicate the exam day as closely as possible. That means taking the test timed (the GMATPrep software does this for you), in one sitting, and in a quiet place with few interruptions. Doing so helps ensure you get an accurate practice score.
After taking the practice GMAT test, you’ll automatically receive your GMAT total score. The total score is generally the score that schools are most interested in. For more information about the GMAT total score, check out our guide.

Step 3: Figure Out How Much Time You Should Study to Meet Your Goal GMAT Score
Taking a practice test helps determine your baseline (or, starting) score. Now that you’ve figured that out, you’ll want to compare it to your goal score. Figure out how many points you are away from meeting your school score by subtracting your practice test score from your goal score.
Below are some estimates of how long to study for the GMAT based on how many points you need to improve:
- 0 – 50 point improvement: 50 hours
- 51 – 100 point improvement: 100 hours
- 101 – 150 point improvement: 150 hours
These are rough estimates based on current data, and will be a little bit different for each test-taker. However, its a good place to start. It’s usually easier for test-takers scoring at 500 or less on their baseline to make larger improvements, while test-takers scoring at 600 or more have a harder time making big gains.
Trying to improve over 150 points will likely be difficult and time-consuming. This would be a huge jump in the GMAT percentiles – for example, improving from a 500 to a 650 takes you from the 30th percentile to the 76th percentile – jumping over nearly half the population! So if you’re looking to make very substantial score improvements, you might want to think about hiring a personal tutor to help, and you’ll have to work hard.
Want to improve your GMAT score by 60 points?
We have the industry's leading GMAT prep program. Built by Harvard, MIT, Stanford, and Wharton alumni and GMAT 99th percentile scorers, the program learns your strengths and weaknesses and customizes a curriculum so you get the most effective prep possible.

How Long Should You Study for the GMAT?
Once you’ve determined your goal score and taken a practice test, the next step is to figure out how long you need to study and build a solid plan to meet your goals.
Step 1: Figure Out How Many Hours You Need to Study
Use the information in the section above to figure out how many hours you need to study for the GMAT based on how many points you want to improve your score.
Step 2: Adjust the Hours You Need to Study (If Necessary)
You may or may not need to make adjustments to the number of total hours you need to study based on your current state of preparation and your goals.
For instance, if you’ve already studied a lot, but still haven’t made any movement towards your goal score, you may want to add another 15-20 hours to the total time you need to study. Traditionally, the more studying you’ve already put in, the harder it may be to raise your score. Usually, the first hours of studying are the most productive, because you’ll make quick gains by fixing errors like careless mistakes or learning how to deal with an unfamiliar question type.
You can also adjust your hours based on your own strengths and weaknesses as a student. Are you a fast learner? If so, you may want to decrease the total time needed by 10 – 15 hours. If you need to see material multiple times for it to sink in, you may want to consider adding hours to your plan.

Step 3: Figure Out How Many Hours You Can Study in a Week
The next step in creating your study plan is to figure out how many hours each week you can spend studying.
It’s important to be realistic about this. You want your study time to be productive. You also want to make sure that you’re not neglecting your other work or responsibilities in order to study; after all, your GMAT application is based on more than just your GMAT score. If you set a practice schedule that’s too packed, you might end up frustrated and burned out.
It’s generally more important to put in more hours than more weeks. That is, it’s better to study 120 hours over twelve weeks than 80 hours over fifteen weeks. However, how much time you can commit to per week also depends on your goals and responsibilities. If trying to cram in 30 hours per week will make you neglect other work, it’s better to stick to 15 hours of studying per week and make sure to excel at your other responsibilities.
Generally, the more hours you can study the GMAT in a week, the fewer weeks you’ll need to study. Remember, however, that your studying needs to be purposeful and useful. Trying to study for 20 hours in one weekend probably won’t help too much. Fitting too much studying into a short period of time will tire you out.
Along the same lines, you want to have a rigorous and consistent schedule week to week. Studying for just one hour once a week will probably lead to gaps as you forget what you learned from the week before. Set a consistent number of hours per week that is rigorous, but not overbearing.
Step 4: Figure Out How Many Weeks You Need to Study
Now that you know how many hours you can study in a week and how many hours you need to study total, it’s time to figure out how many weeks you need to study. Divide the total number of hours you need to study the GMAT by the number of hours you can study each week. That’s the number of weeks you need to study.
For example, if you need to study 120 hours and you can study for 10 hours each week, you will need to study for 12 weeks.
When planning your GMAT study schedule, you may also want to build in time for retakes. You can take the GMAT up to five times in a 12 month period, but you have to wait for at least 16 days between exams. If you think you’re going to want to retake the GMAT exam, add in at least four weeks per retake so you can make improvements based on where you went wrong.
Want to Identify YOUR GMAT Strengths and Weaknesses?
Our proprietary GMAT Diagnostic Assessment creates a customized study plan for you that takes you from registration all the way to test day! It is included with every account and proven to significantly maximize your score.
Get your personalized assessment as part of your 5 day risk-free trial now:

Step 5: Double-Check Application Deadlines
Double-check the application deadlines for your schools. If you choose which schools to send your test scores before you take the GMAT, the schools will receive your scores in less than 20 days. So, to be safe, schedule your GMAT at least three weeks before application deadlines.
Putting that all together, if you need 12 weeks to study for the GMAT, plus four weeks for re-takes and three weeks for schools to receive your score, you’re going to want to start studying about 19 weeks before your exam.
If you can’t fit in your studying before the application is due, you have a few options. First, you can eliminate a retake from your schedule and focus on acing the test the first time around. Second, you can try to fit more hours of prep each week. The more hours you study each week, the fewer weeks you’ll need to study.
Step 6: Create Your GMAT Study Schedule
Now that you know when to start studying, how many weeks you’ll be studying, and how many hours you’ll be studying each week, it’s time to create a study schedule to help you reach your score goals.
Try to schedule your study times for the same times and days each week. This helps you plan your schedule and work consistently. For instance, if you need to schedule for fifteen hours per week, you can study for three hours every Monday – Friday, or for five hours every Wednesday, Saturday, and Sunday. Setting the same dates and times for practice helps build consistency into your routine.
Make sure you plan regular practice tests as part of your study plan. Taking regular practice tests helps to track your progress and ensure you’re on track to meet your targets.

Final Verdict: How Long Should I Study for the GMAT?
How long does it take to prepare for the GMAT? The answer to that question varies for each test-taker. Some people spend months studying, while others barely prepare at all.
The key to deciding how long to study for the GMAT is figuring out your goal score and how much you need to improve to hit that goal. From there you can determine the number of hours you need to study and how long you need to get that amount of GMAT prep in. Finally, you should create a GMAT study schedule to help you track your progress and stick to your plan.
What’s Next?
What’s a good score for the GMAT? Learn more about how to set your personalized GMAT score goal by reading out our guide.
Once you’ve set a good study schedule, check out our guide to picking a GMAT test date.
If you’re getting ready to register for the GMAT, make sure you check out our step-by-step GMAT registration guide.
 PrepScholar GMAT
PrepScholar GMAT